高级IOS开发进阶 - 自旋锁、互斥锁以及读写锁!(二)
4.3 源码分析
initWithCondition:
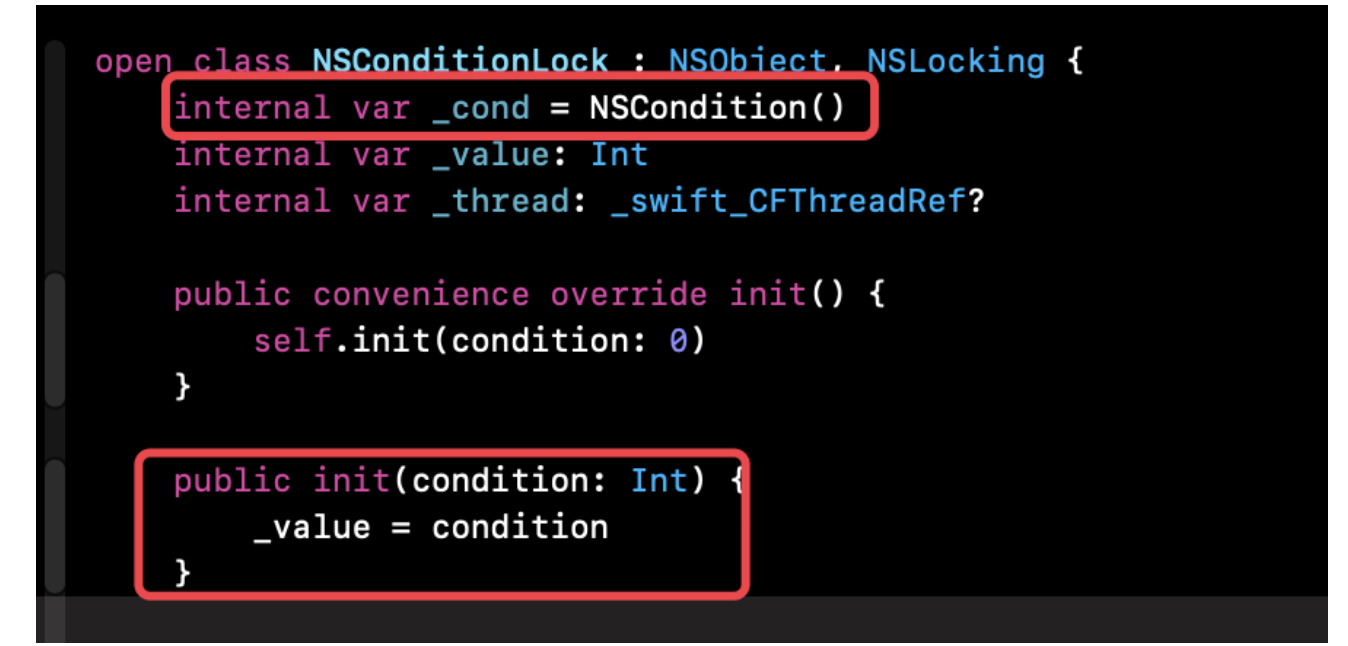
- 保存了
condition参数以及NSCondition的创建。 lockWhenCondition:
open func lock(whenCondition condition: Int) {
let _ = lock(whenCondition: condition, before: Date.distantFuture)
}内部调用了lockWhenCondition: before:,默认值传的Date.distantFuture:
open func lock(whenCondition condition: Int, before limit: Date) -> Bool {
_cond.lock()
while _thread != nil || _value != condition {
if !_cond.wait(until: limit) {
_cond.unlock()
return false
}
}
_thread = pthread_self()
_cond.unlock()
return true
}NSCondition加锁判断condition条件是否满足,不满足调用NSCondition的wait waitUntilDate方法进入等待,超时后解锁返回false。满足的情况下赋值_thread解锁返回true。
unlockWithCondition:
open func unlock(withCondition condition: Int) {
_cond.lock()
_thread = nil
_value = condition
_cond.broadcast()
_cond.unlock()
}加锁后释放_thread,更新condition,调用broadcast后解锁。
lock
open func lock() {
let _ = lock(before: Date.distantFuture)
}
open func lock(before limit: Date) -> Bool {
_cond.lock()
while _thread != nil {
if !_cond.wait(until: limit) {
_cond.unlock()
return false
}
}
_thread = pthread_self()
_cond.unlock()
return true
}判断是否有其它任务阻塞,没有阻塞直接创建_thread返回true。
unlock
open func unlock() {
_cond.lock()
_thread = nil
_cond.broadcast()
_cond.unlock()
}广播并且释放_thread。
4.4 反汇编分析
initWithCondition:
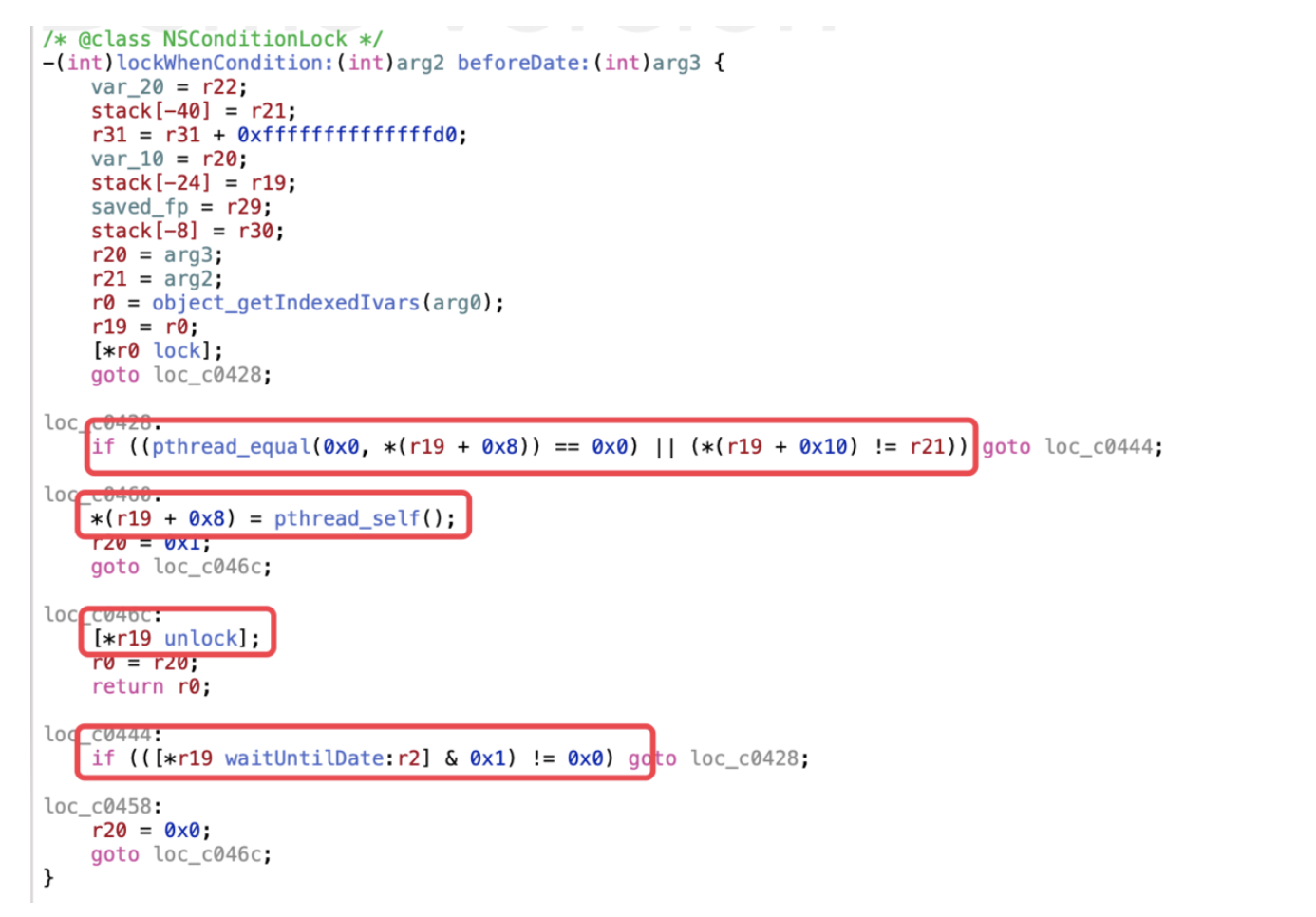
lockWhenCondition:
-(int)lockWhenCondition:(int)arg2 {
r0 = [arg0 lockWhenCondition:arg2 beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]];
return r0;
}调用自己的lockWhenCondition: beforeDate ::
-(int)unlockWithCondition:(int)arg2 {
r0 = object_getIndexedIvars(arg0);
[*r0 lock];
*(int128_t *)(r0 + 0x8) = 0x0;
*(int128_t *)(r0 + 0x10) = arg2;
[*r0 broadcast];
r0 = *r0;
r0 = [r0 unlock];
return r0;
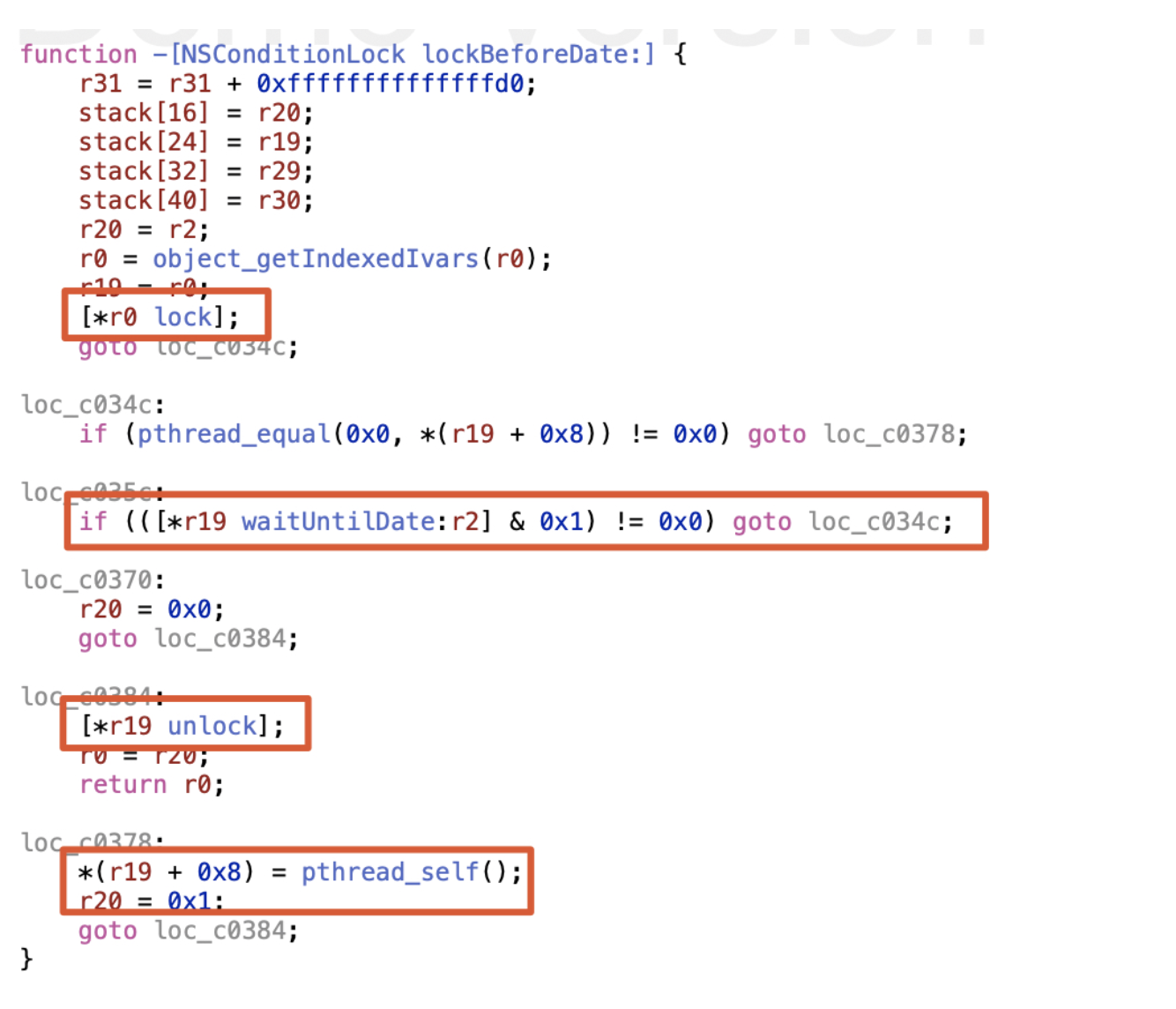
}lock:
int -[NSConditionLock lock](int arg0) {
r0 = [arg0 lockBeforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]];
return r0;
}
int -[NSConditionLock unlock]() {
r0 = object_getIndexedIvars(r0);
[*r0 lock];
*(r0 + 0x8) = 0x0;
[*r0 broadcast];
r0 = *r0;
r0 = [r0 unlock];
return r0;
}汇编、源码以及断点调试逻辑相同。
NSConditionLock 内部封装了NSCondition。
五、OSSpinLock & os_unfair_lock
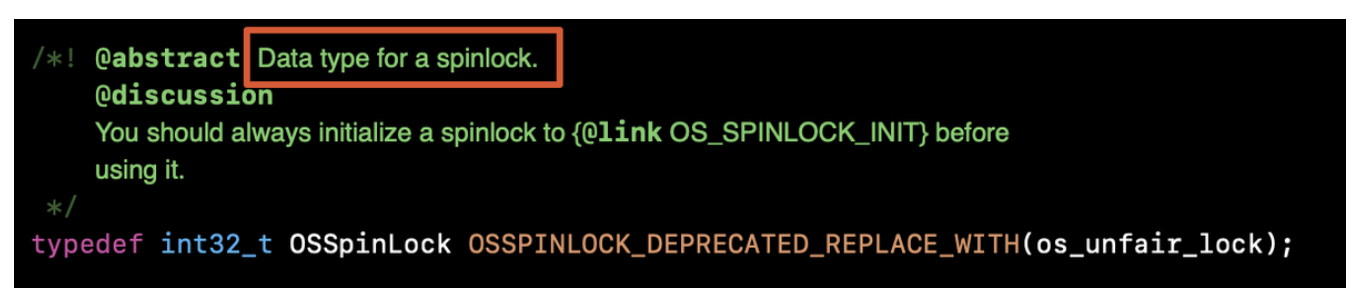
OSSpinLock的API注释以及它自己的命名说明了这是一把自旋锁,自iOS10之后被os_unfair_lock替代。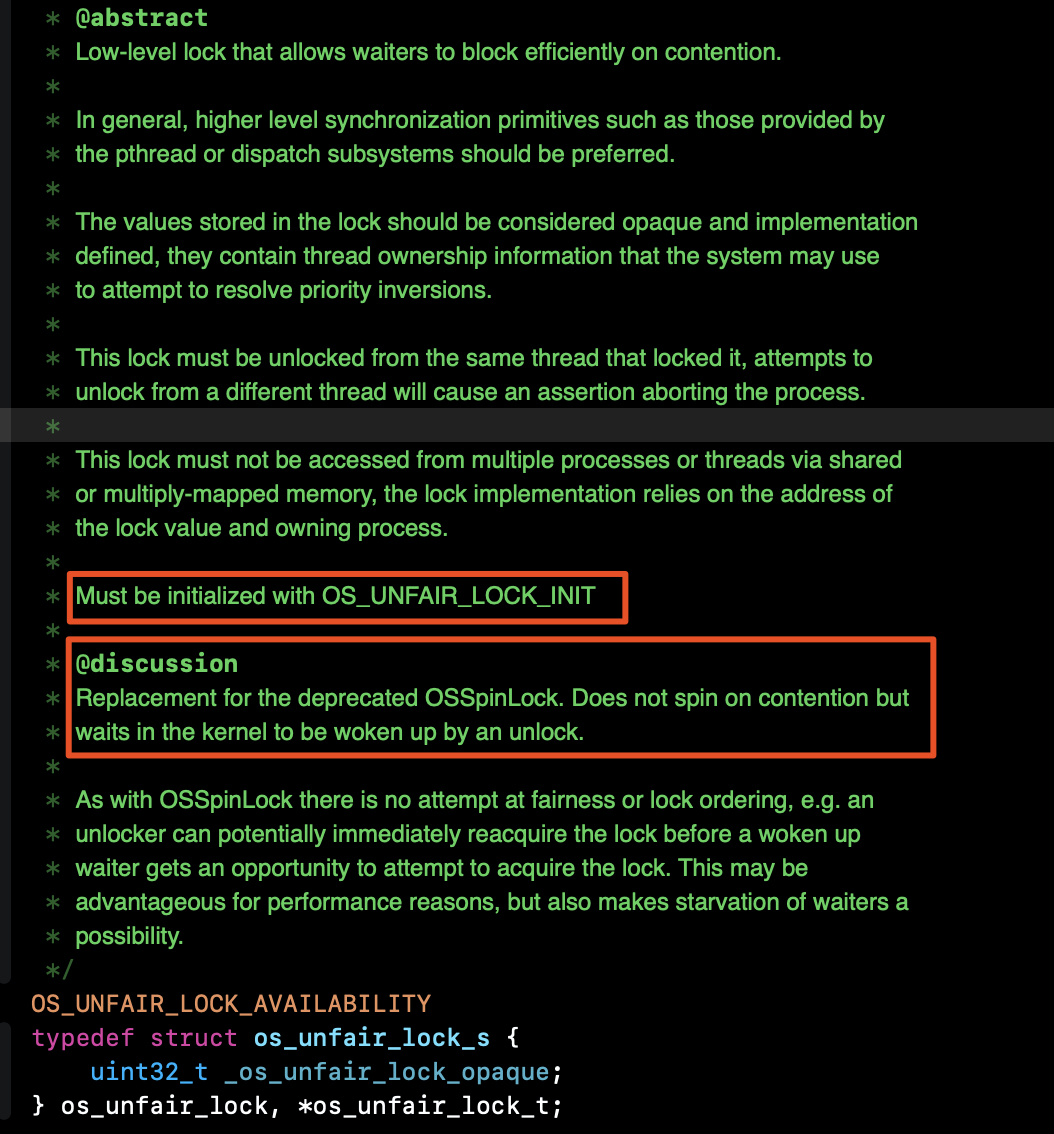
os_unfair_lock必须以OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_INIT初始化。- 它是用来代替
OSSpinLock的。 - 它不是自旋锁(忙等),是被内核唤醒的(闲等)。
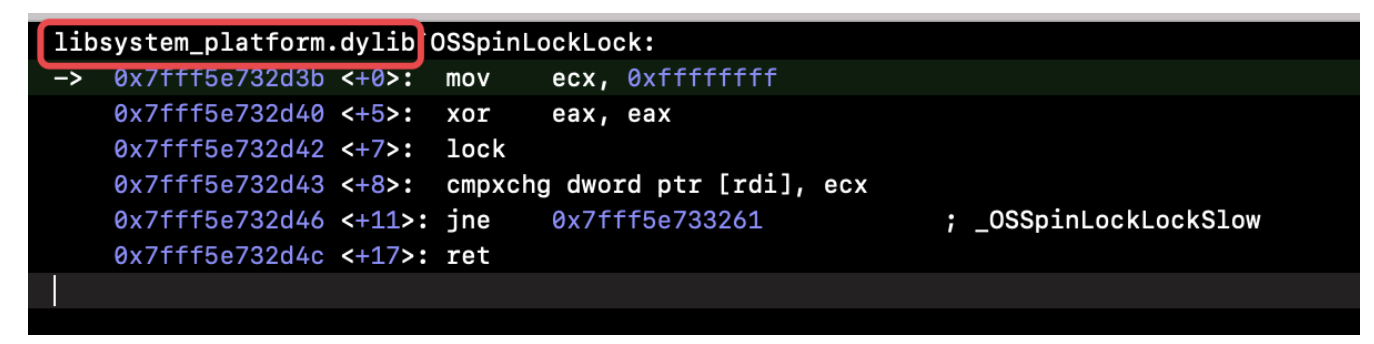
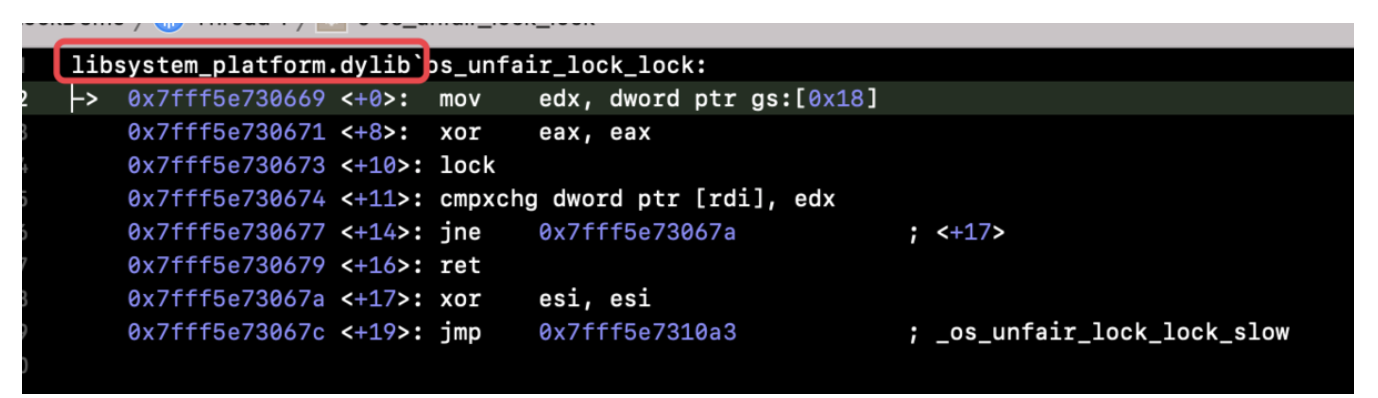
libsystem_platform.dylib中的。可以在openSource中找到他们libplatform的源码libplatform,实现是在/src/os目录下的lock.c文件中。5.1 OSSpinLock 源码分析
OSSpinLock的使用一般会用到以下API:
OSSpinLock hp_spinlock = OS_SPINLOCK_INIT;
OSSpinLockLock(&hp_spinlock);
OSSpinLockUnlock(&hp_spinlock);typedef int32_t OSSpinLock OSSPINLOCK_DEPRECATED_REPLACE_WITH(os_unfair_lock);
#define OS_SPINLOCK_INIT 0OSSpinLock本身是一个int32_t类型的值,初始化默认值为0。
5.1.1 OSSpinLockLock
void
OSSpinLockLock(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS(spin_lock, OSSpinLockLock);
OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS(_spin_lock, OSSpinLockLock);
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchg(l, 0, _OSSpinLockLocked, acquire);
if (likely(r)) return;
return _OSSpinLockLockSlow(l);
}
#if TARGET_OS_IPHONE && !TARGET_OS_SIMULATOR
static const OSSpinLock _OSSpinLockLocked = 1;
#else
static const OSSpinLock _OSSpinLockLocked = -1;
#endifOS_ATOMIC_ALIAS定义如下:
#undef OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS
#define OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS(n, o)
static void _OSSpinLockLock(volatile OSSpinLock *l);这里相当于分了两条路径,通过_OSSpinLockLocked标记是否被锁定。在源码中并没有找到_OSSpinLockLock函数的实现。
5.1.1.1 _OSSpinLockLockSlow
#if OS_ATOMIC_UP
void
_OSSpinLockLockSlow(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
return _OSSpinLockLockYield(l); // Don't spin on UP
}
#elif defined(__arm64__)
// Exclusive monitor must be held during WFE <rdar://problem/22300054>
#if defined(__ARM_ARCH_8_2__)
void
_OSSpinLockLockSlow(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
uint32_t tries = OS_LOCK_SPIN_SPIN_TRIES;
OSSpinLock lock;
_spin:
while (unlikely(lock = os_atomic_load_exclusive(l, relaxed))) {
if (unlikely(lock != _OSSpinLockLocked)) {
os_atomic_clear_exclusive();
return _os_lock_corruption_abort((void *)l, (uintptr_t)lock);
}
if (unlikely(!tries--)) {
os_atomic_clear_exclusive();
return _OSSpinLockLockYield(l);
}
OS_LOCK_SPIN_PAUSE();
}
os_atomic_clear_exclusive();
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchg(l, 0, _OSSpinLockLocked, acquire);
if (likely(r)) return;
goto _spin;
}
#else // !__ARM_ARCH_8_2__
void
_OSSpinLockLockSlow(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
uint32_t tries = OS_LOCK_SPIN_SPIN_TRIES;
OSSpinLock lock;
os_atomic_rmw_loop(l, lock, _OSSpinLockLocked, acquire, if (unlikely(lock)){
if (unlikely(lock != _OSSpinLockLocked)) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up(return
_os_lock_corruption_abort((void *)l, (uintptr_t)lock));
}
if (unlikely(!tries--)) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up(return _OSSpinLockLockYield(l));
}
OS_LOCK_SPIN_PAUSE();
continue;
});
}
#endif // !__ARM_ARCH_8_2__
#else // !OS_ATOMIC_UP
void
_OSSpinLockLockSlow(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
uint32_t tries = OS_LOCK_SPIN_SPIN_TRIES;
OSSpinLock lock;
while (unlikely(lock = *l)) {
_spin:
if (unlikely(lock != _OSSpinLockLocked)) {
return _os_lock_corruption_abort((void *)l, (uintptr_t)lock);
}
if (unlikely(!tries--)) return _OSSpinLockLockYield(l);
OS_LOCK_SPIN_PAUSE();
}
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchgv(l, 0, _OSSpinLockLocked, &lock, acquire);
if (likely(r)) return;
goto _spin;
}
#endif // !OS_ATOMIC_UP可以看到内部有自转逻辑,这里直接分析_OSSpinLockLockYield
5.1.1.2 _OSSpinLockLockYield
static void
_OSSpinLockLockYield(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
int option = SWITCH_OPTION_DEPRESS;
mach_msg_timeout_t timeout = 1;
uint64_t deadline = _os_lock_yield_deadline(timeout);
OSSpinLock lock;
while (unlikely(lock = *l)) {
_yield:
if (unlikely(lock != _OSSpinLockLocked)) {
_os_lock_corruption_abort((void *)l, (uintptr_t)lock);
}
thread_switch(MACH_PORT_NULL, option, timeout);
if (option == SWITCH_OPTION_WAIT) {
timeout++;
} else if (!_os_lock_yield_until(deadline)) {
option = SWITCH_OPTION_WAIT;
}
}
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchgv(l, 0, _OSSpinLockLocked, &lock, acquire);
if (likely(r)) return;
goto _yield;
}内部有超时时间以及线程切换逻辑。
5.1.2 OSSpinLockUnlock
void
OSSpinLockUnlock(volatile OSSpinLock *l)
{
OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS(spin_unlock, OSSpinLockUnlock);
OS_ATOMIC_ALIAS(_spin_unlock, OSSpinLockUnlock);
return _os_nospin_lock_unlock((_os_nospin_lock_t)l);
}内部调用了_os_nospin_lock_unlock。
5.1.2.1 _os_nospin_lock_unlock
void
_os_nospin_lock_unlock(_os_nospin_lock_t l)
{
os_lock_owner_t self = _os_lock_owner_get_self();
os_ulock_value_t current;
current = os_atomic_xchg(&l->oul_value, OS_LOCK_NO_OWNER, release);
if (likely(current == self)) return;
return _os_nospin_lock_unlock_slow(l, current);
}_os_nospin_lock_unlock_slow:
static void
_os_nospin_lock_unlock_slow(_os_nospin_lock_t l, os_ulock_value_t current)
{
os_lock_owner_t self = _os_lock_owner_get_self();
if (unlikely(OS_ULOCK_OWNER(current) != self)) {
return; // no unowned_abort for drop-in compatibility with OSSpinLock
}
if (current & OS_ULOCK_NOWAITERS_BIT) {
__LIBPLATFORM_INTERNAL_CRASH__(current, "unlock_slow with no waiters");
}
for (;;) {
int ret = __ulock_wake(UL_COMPARE_AND_WAIT | ULF_NO_ERRNO, l, 0);
if (unlikely(ret < 0)) {
switch (-ret) {
case EINTR:
continue;
case ENOENT:
break;
default:
__LIBPLATFORM_INTERNAL_CRASH__(-ret, "ulock_wake failure");
}
}
break;
}
}5.2 os_unfair_lock 源码分析
typedef struct os_unfair_lock_s {
uint32_t _os_unfair_lock_opaque;
} os_unfair_lock, *os_unfair_lock_t;初始化OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_INIT直接设置了默认值0:
#define OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_INIT ((os_unfair_lock){0})5.2.1 os_unfair_lock_lock
void
os_unfair_lock_lock(os_unfair_lock_t lock)
{
_os_unfair_lock_t l = (_os_unfair_lock_t)lock;
os_lock_owner_t self = _os_lock_owner_get_self();
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchg(&l->oul_value, OS_LOCK_NO_OWNER, self, acquire);
if (likely(r)) return;
return _os_unfair_lock_lock_slow(l, OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_NONE, self);
}_os_lock_owner_get_self:
OS_ALWAYS_INLINE OS_CONST
static inline os_lock_owner_t
_os_lock_owner_get_self(void)
{
os_lock_owner_t self;
self = (os_lock_owner_t)_os_tsd_get_direct(__TSD_MACH_THREAD_SELF);
return self;
}_os_unfair_lock_lock_slow:
static void
_os_unfair_lock_lock_slow(_os_unfair_lock_t l,
os_unfair_lock_options_t options, os_lock_owner_t self)
{
os_unfair_lock_options_t allow_anonymous_owner =
options & OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_ALLOW_ANONYMOUS_OWNER;
options &= ~OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_ALLOW_ANONYMOUS_OWNER;
if (unlikely(options & ~OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_OPTIONS_MASK)) {
__LIBPLATFORM_CLIENT_CRASH__(options, "Invalid options");
}
os_ulock_value_t current, new, waiters_mask = 0;
while (unlikely((current = os_atomic_load(&l->oul_value, relaxed)) !=
OS_LOCK_NO_OWNER)) {
_retry:
if (unlikely(OS_ULOCK_IS_OWNER(current, self, allow_anonymous_owner))) {
return _os_unfair_lock_recursive_abort(self);
}
new = current & ~OS_ULOCK_NOWAITERS_BIT;
if (current != new) {
// Clear nowaiters bit in lock value before waiting
if (!os_atomic_cmpxchgv(&l->oul_value, current, new, ¤t,
relaxed)){
continue;
}
current = new;
}
int ret = __ulock_wait(UL_UNFAIR_LOCK | ULF_NO_ERRNO | options,
l, current, 0);
if (unlikely(ret < 0)) {
switch (-ret) {
case EINTR:
case EFAULT:
continue;
case EOWNERDEAD:
_os_unfair_lock_corruption_abort(current);
break;
default:
__LIBPLATFORM_INTERNAL_CRASH__(-ret, "ulock_wait failure");
}
}
if (ret > 0) {
// If there are more waiters, unset nowaiters bit when acquiring lock
waiters_mask = OS_ULOCK_NOWAITERS_BIT;
}
}
new = self & ~waiters_mask;
bool r = os_atomic_cmpxchgv(&l->oul_value, OS_LOCK_NO_OWNER, new,
¤t, acquire);
if (unlikely(!r)) goto _retry;
}内部是wait等待逻辑。
5.2.2 os_unfair_lock_unlock
void
os_unfair_lock_unlock(os_unfair_lock_t lock)
{
_os_unfair_lock_t l = (_os_unfair_lock_t)lock;
os_lock_owner_t self = _os_lock_owner_get_self();
os_ulock_value_t current;
current = os_atomic_xchg(&l->oul_value, OS_LOCK_NO_OWNER, release);
if (likely(current == self)) return;
return _os_unfair_lock_unlock_slow(l, self, current, 0);
}内部调用了_os_unfair_lock_unlock_slow:
OS_NOINLINE
static void
_os_unfair_lock_unlock_slow(_os_unfair_lock_t l, os_lock_owner_t self,
os_ulock_value_t current, os_unfair_lock_options_t options)
{
os_unfair_lock_options_t allow_anonymous_owner =
options & OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_ALLOW_ANONYMOUS_OWNER;
options &= ~OS_UNFAIR_LOCK_ALLOW_ANONYMOUS_OWNER;
if (unlikely(OS_ULOCK_IS_NOT_OWNER(current, self, allow_anonymous_owner))) {
return _os_unfair_lock_unowned_abort(OS_ULOCK_OWNER(current));
}
if (current & OS_ULOCK_NOWAITERS_BIT) {
__LIBPLATFORM_INTERNAL_CRASH__(current, "unlock_slow with no waiters");
}
for (;;) {
int ret = __ulock_wake(UL_UNFAIR_LOCK | ULF_NO_ERRNO, l, 0);
if (unlikely(ret < 0)) {
switch (-ret) {
case EINTR:
continue;
case ENOENT:
break;
default:
__LIBPLATFORM_INTERNAL_CRASH__(-ret, "ulock_wake failure");
}
}
break;
}
}可以看到内部是有唤醒逻辑的。
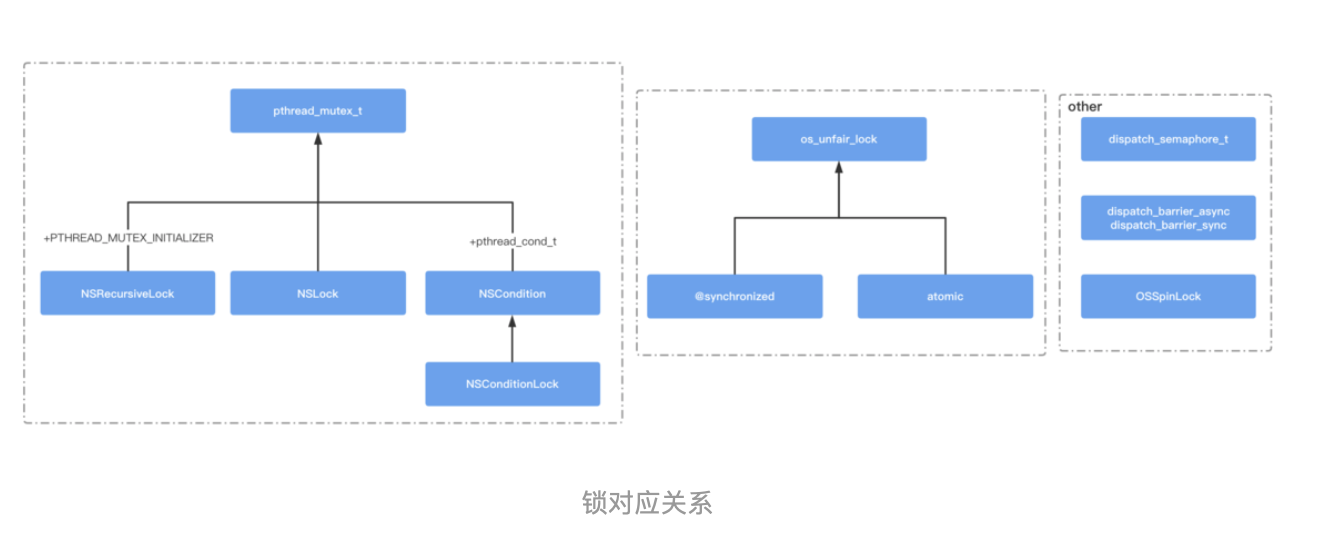
六、读写锁
读操作可以共享,写操作是排他的,读可以有多个在读,写只有唯一个在写,同时写的时候不允许读。要实现读写锁核心逻辑是:
- 多读单写
- 写写互斥
- 读写互斥
- 写不能阻塞任务执行
有两套方案:
- 1.使用 栅栏函数 相关
API。 - 2.使用
pthread_rwlock_t相关API。
6.1 dispatch_barrier_async 实现多读单写
写:通过栅栏函数可以实现写写互斥以及读写互斥,写使用async可以保证写逻辑不阻塞当前任务执行。
读:使用dispatch_sync同步效果实现多读(放入并发队列中)。
- 首先定义一个并发队列以及字典存储数据:
@property (nonatomic, strong) dispatch_queue_t concurrent_queue;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary *dataDic;
//初始化
self.concurrent_queue = dispatch_queue_create("rw_queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
self.dataDic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];- 写入操作:
- (void)safeSetter:(NSString *)name time:(int)time {
dispatch_barrier_async(self.concurrent_queue, ^{
sleep(time);
[self.dataDic setValue:name forKey:@"HotpotCat"];
NSLog(@"write name:%@,currentThread:%@",name,[NSThread currentThread]);
});
}为了方便测试key值写死,并且传入一个time。barrier保证了写之间互斥以及读写互斥。
- 读取操作:
- (NSString *)safeGetterWithTime:(int)time {
__block NSString *result;
//多条线程同时读,阻塞的是当前线程,多条线程访问就是多读了。同步使用concurrent_queue是为了配合栅栏函数读写互斥。
dispatch_sync(self.concurrent_queue, ^{
sleep(time);
result = self.dataDic[@"HotpotCat"];
});
NSLog(@"result:%@,currentThread:%@,time:%@",result,[NSThread currentThread],@(time));
return result;
}使用同步函数配合栅栏函数(栅栏函数只能针对同一队列)实现读写互斥,当多条线程同时访问safeGetterWithTime时就实现了多读操作。
- 写入验证:
//调用
[self safeSetter:@"1" time:4];
[self safeSetter:@"2" time:1];
[self safeSetter:@"3" time:2];
[self safeSetter:@"4" time:1];输出:
write name:1,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281fea4c0>{number = 5, name = (null)}
write name:2,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281fea4c0>{number = 5, name = (null)}
write name:3,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281fea4c0>{number = 5, name = (null)}
write name:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281fea4c0>{number = 5, name = (null)}很明显写之间是互斥的,任务1没有执行完之前其它任务都在等待。
- 读取验证:
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
NSString *result = [self safeGetterWithTime:5 - i];
NSLog(@"result:%@",result);
});
}输出:
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281f80600>{number = 7, name = (null)},time:1
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281fce540>{number = 8, name = (null)},time:2
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281f80980>{number = 9, name = (null)},time:3
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281feb540>{number = 10, name = (null)},time:4
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x281f80a80>{number = 11, name = (null)},time:5任务并行执行,顺序是由于设置了sleep时间,如果去掉时间或者时间一致,每次执行结果都不同了。
6.2 pthread_rwlock_t 实现多读单写
- 定义锁以及字典数据:
{
pthread_rwlock_t rw_lock;
pthread_rwlockattr_t rw_lock_attr;
}
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary *dataDic;pthread_rwlockattr_t读写属性有两种:lockkind与pshared。lockkind:读写策略,包括读取优先(默认属性)、写入优先。苹果系统里面没有提供 pthread_rwlockattr_getkind_np 与 pthread_rwlockattr_setkind_np 相关函数。pshared:PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE(进程内竞争读写锁,默认属性)PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED(进程间竞争读写锁)
- 初始化:
self.dataDic = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
//初始化
pthread_rwlockattr_init(&rw_lock_attr);
pthread_rwlock_init(&rw_lock, &rw_lock_attr);
//进程内
pthread_rwlockattr_setpshared(&rw_lock_attr, PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE);- 写入操作如下:
- (void)safeSetter:(NSString *)name {
//写锁
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rw_lock);
[self.dataDic setValue:name forKey:@"HotpotCat"];
NSLog(@"write name:%@,currentThread:%@",name,[NSThread currentThread]);
//释放
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rw_lock);
}- 读取操作如下:
- (NSString *)safeGetter {
//读锁
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rw_lock);
NSString *result = self.dataDic[@"HotpotCat"];
//释放
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rw_lock);
NSLog(@"result:%@,currentThread:%@",result,[NSThread currentThread]);
return result;
}- 写入验证:
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
[self safeSetter:@"1"];
});
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
[self safeSetter:@"2"];
});
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
[self safeSetter:@"3"];
});
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
[self safeSetter:@"4"];
});输出:
LockDemo[52251:5873172] write name:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x60000072e980>{number = 4, name = (null)}
LockDemo[52251:5873177] write name:1,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x60000075d100>{number = 6, name = (null)}
LockDemo[52251:5873170] write name:2,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x60000072f600>{number = 7, name = (null)}
LockDemo[52251:5873178] write name:3,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x60000073d480>{number = 5, name = (null)}这里就与队列调度有关了,顺序不定,如果不加锁大量并发调用下则会crash。
- 读取验证:
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
NSString *result = [self safeGetter];
});
}输出:
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x600001cdc200>{number = 5, name = (null)}
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x600001cd1080>{number = 7, name = (null)}
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x600001c95f40>{number = 6, name = (null)}
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x600001c91ec0>{number = 3, name = (null)}
result:4,currentThread:<NSThread: 0x600001c94d80>{number = 4, name = (null)}输出顺序也不一定。当然混合读写测试也可以,用数组更容易测试。
对于读数据比修改数据频繁的应用,用读写锁代替互斥锁可以提高效率。因为使用互斥锁时,即使是读出数据(相当于操作临界区资源)都要上互斥锁,而采用读写锁,则可以在任一时刻允许多个读出者存在,提高了更高的并发度,同时在某个写入者修改数据期间保护该数据,以免任何其它读出者或写入者的干扰。
获取一个读写锁用于读称为共享锁,获取一个读写锁用于写称为独占锁,因此对于某个给定资源的共享访问也称为共享-独占上锁。
作者:HotPotCat
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f8e5f0d0b23
