iOS MachO文件
一、MachO文件概述
Mach-O(Mach Object)是mac以及iOS上的格式, 类似于windows上的PE格式 (Portable Executable ),linux上的elf格式 (Executable and Linking Format)。
Mach-O是一种用于可执行文件、目标代码、动态库的文件格式。作为a.out格式的替代,Mach-O提供了更强的扩展性。
1.1 MachO格式的常见文件
- 目标文件
.o - 库文件
.a.dylibFramework- 可执行文件
dyld.dsym
1.2 格式验证
1.2.1 .o、.out、可执行文件
新建test.c文件,内容如下:
#include
int main() {
printf("test\n");
return 0;
}验证.o文件:
clang -c test.c
//clang -c test.c -isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk-c默认生成a.out,如果报找不到'stdio.h' file not found,则可以指定-isysroot。文章最后有具体的解决方案,通过
file指令查看文件格式:file test.o
test.o: Mach-O 64-bit object x86_64验证a.out可执行文件:
clang test.o
file a.out
a.out: Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64
./a.out
test验证可执行文件:
clang -o test2 test.c
file test2
test2: Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64
./test2
test至此再生成一个test3可执行文件:
clang -o test3 test.o那么生成的a.out、test2、test3一样么?

md5相同。test3的md5应该和test2和a.out相同。源码没有变化,所以应该相同的。在指定-isysroot后生成的可能不同,推测和CommandLineTools有关(系统中一个,Xcode中一个)。再创建一个test1.c文件,内容如下:
#include
void test1Func() {
printf("test1 func \n");
}修改test.c:
#include
void test1Func();
int main() {
test1Func();
printf("test\n");
return 0;
}这个时候相当于有多个文件了,编译生成可执行文件demo、demo1、demo2:
clang -o demo test1.c test.c
clang -c test1.c test.c
clang -o demo1 test.o test1.o
clang -o demo2 test1.o test.o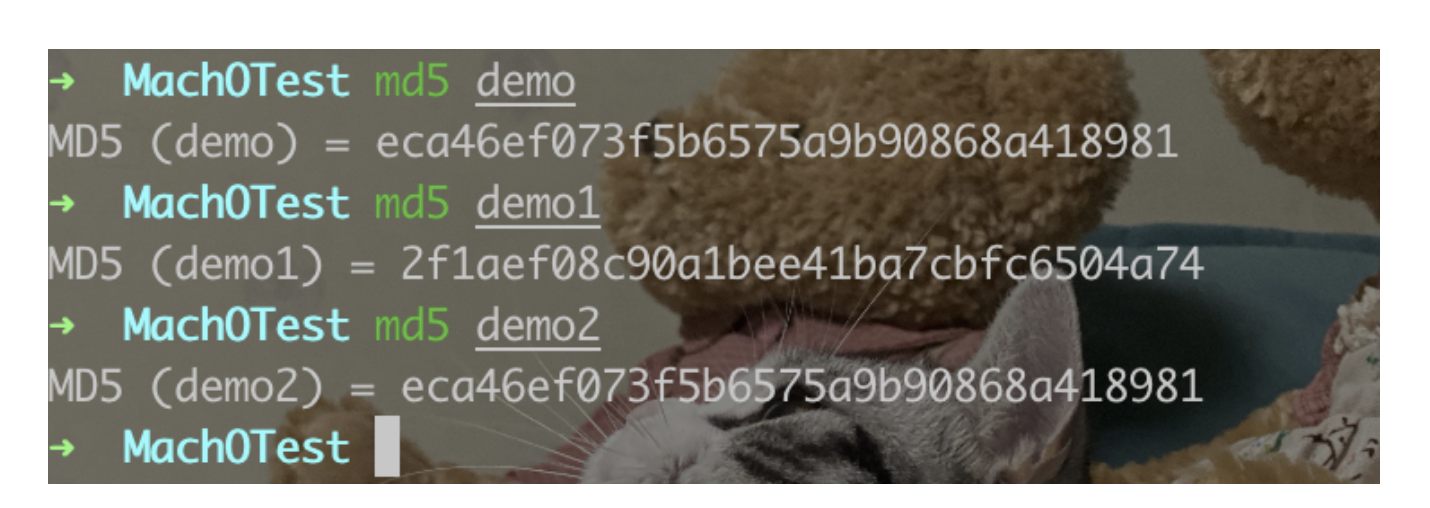
demo1和demo2``md5不同是因为test.o和test1.o顺序不同。objdump --macho -d demo查看下macho:
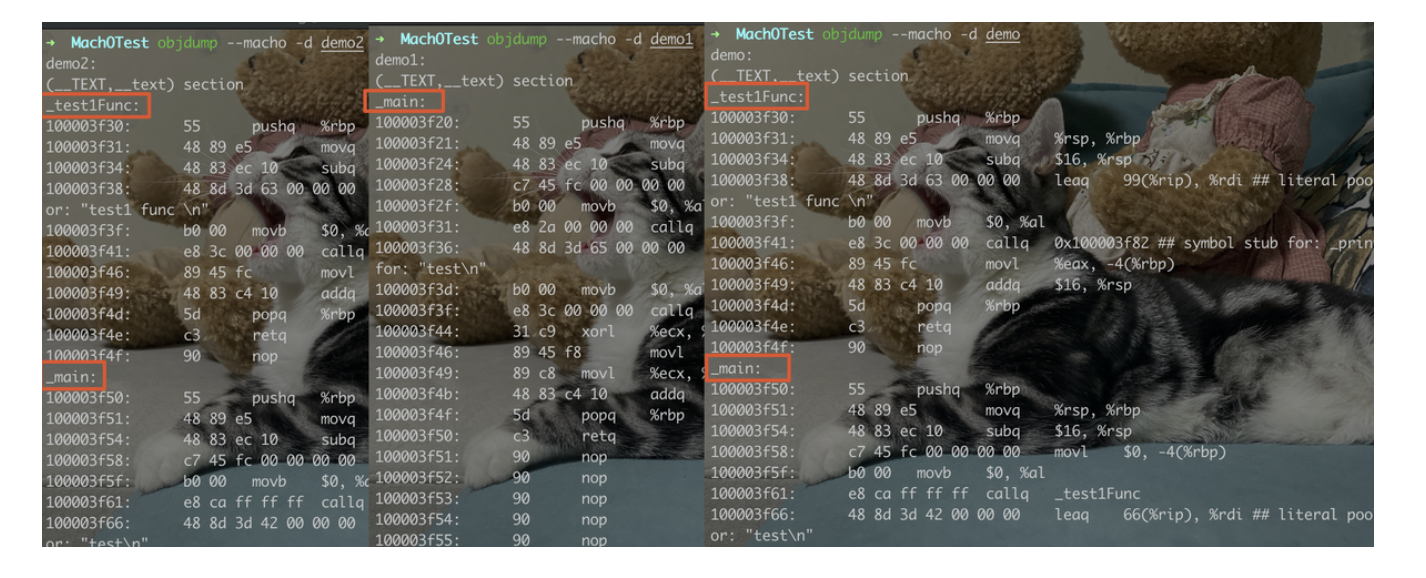
md5不同的原因。这里很像Xcode中Build Phases -> Compile Sources中源文件的顺序。⚠️源文件顺序不同,编译出来的二进制文件不同( 大小相同),二进制排列顺序不同。
1.2.2.a文件
直接创建一个library库查看:
//find /usr -name "*.a"
file libTestLibrary.a
libTestLibrary.a: current ar archive random library1.2.3. .dylib
cd /usr/lib
file dyld
dyld: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [x86_64:Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64] [i386:Mach-O dynamic linker i386]
dyld (for architecture x86_64): Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64
dyld (for architecture i386): Mach-O dynamic linker i3861.2.4 dyld
cd /usr/lib
file dyld
dyld: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [x86_64:Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64] [i386:Mach-O dynamic linker i386]
dyld (for architecture x86_64): Mach-O 64-bit dynamic linker x86_64
dyld (for architecture i386): Mach-O dynamic linker i386这里需要注意的是dyld不是可执行文件,是一个dynamic linker。系统内核触发。
1.2.5 .dsym
file TestDsym.app.dSYM
TestDsym.app.dSYM: directory
cd TestDsym.app.dSYM/Contents/Resources/DWARF
file TestDsym
TestDsym: Mach-O 64-bit dSYM companion file arm64二、可执行文件
MachO:file TestDsym
TestDsym: Mach-O 64-bit executable arm6411以上的系统都只支持64位架构,所以默认就没有32位的)。将Deployment Info改为iOS 10编译再次查看MachO:file TestDsym
TestDsym: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [arm_v7:Mach-O executable arm_v7] [arm64:Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64]
TestDsym (for architecture armv7): Mach-O executable arm_v7
TestDsym (for architecture arm64): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64这个时候就有多个架构了。
当然也可以在Xcode中直观的看到支持的架构:
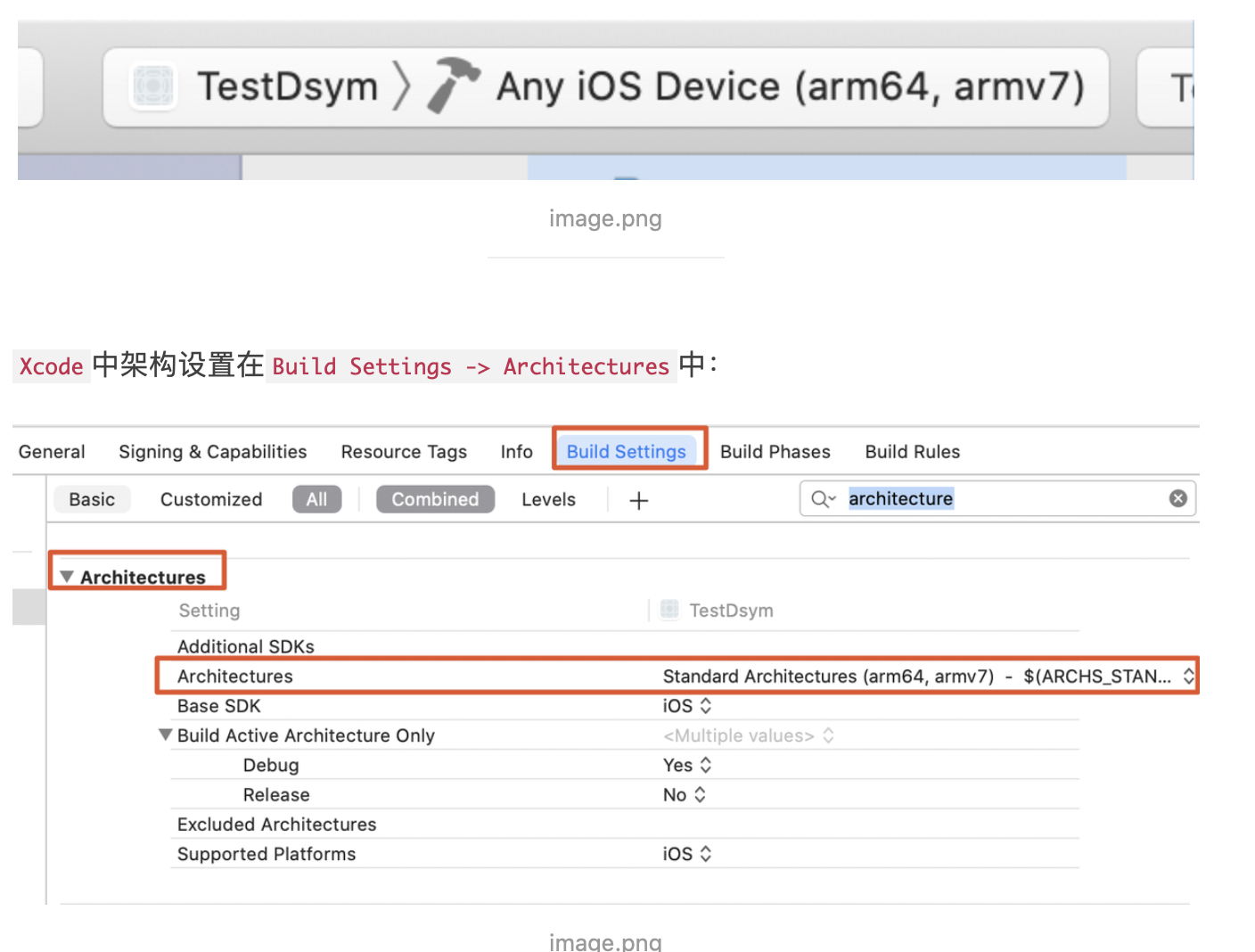
Architectures:支持的架构。Build Active Architecture Only:默认情况下debug模式下只编译当前设备架构,release模式下需要根据支持的设备。$(ARCHS_STANDARD):环境变量,代表当前支持的架构。
如果我们要修改架构直接在Architectures中配置(增加armv7s):
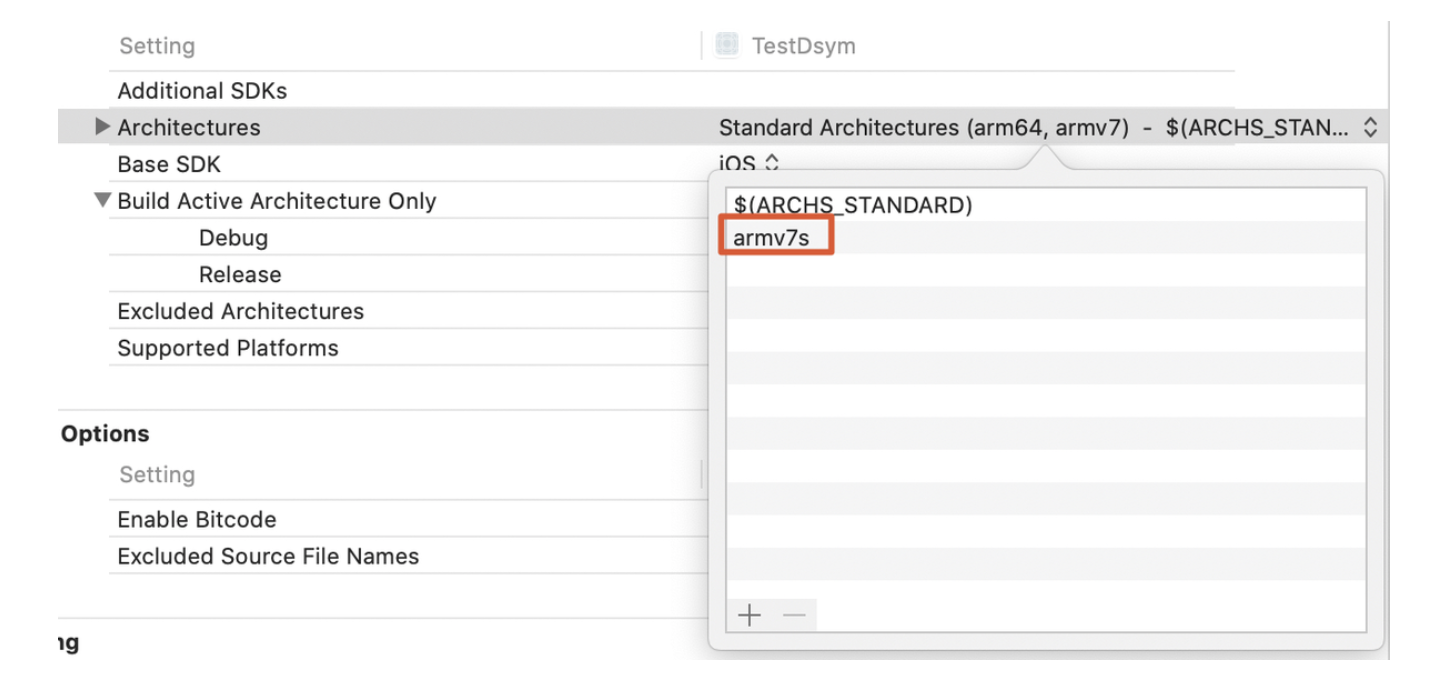
编译再次查看
MachO:file TestDsym
TestDsym: Mach-O universal binary with 3 architectures: [arm_v7:Mach-O executable arm_v7] [arm_v7s:Mach-O executable arm_v7s] [arm64:Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64]
TestDsym (for architecture armv7): Mach-O executable arm_v7
TestDsym (for architecture armv7s): Mach-O executable arm_v7s
TestDsym (for architecture arm64): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm642.1通用二进制文件(Universal binary)
- 苹果公司提出的一种程序代码,能同时适用多种架构的二进制文件。
- 同一个程序包中同时为多种架构提供最理想的性能。
- 因为需要储存多种代码,通用二进制应用程序通常比单一平台二进制的程序要大。
- 由于多种架构有共同的非执行资源(代码以外的),所以并不会达到单一版本的多倍之多(特殊情况下,只有少量代码文件的情况下有可能会大于多倍)。
- 由于执行中只调用一部分代码,运行起来不需要额外的内存。
当我们将通用二进制文件拖入Hopper时,能够看到让我们选择对应的架构:
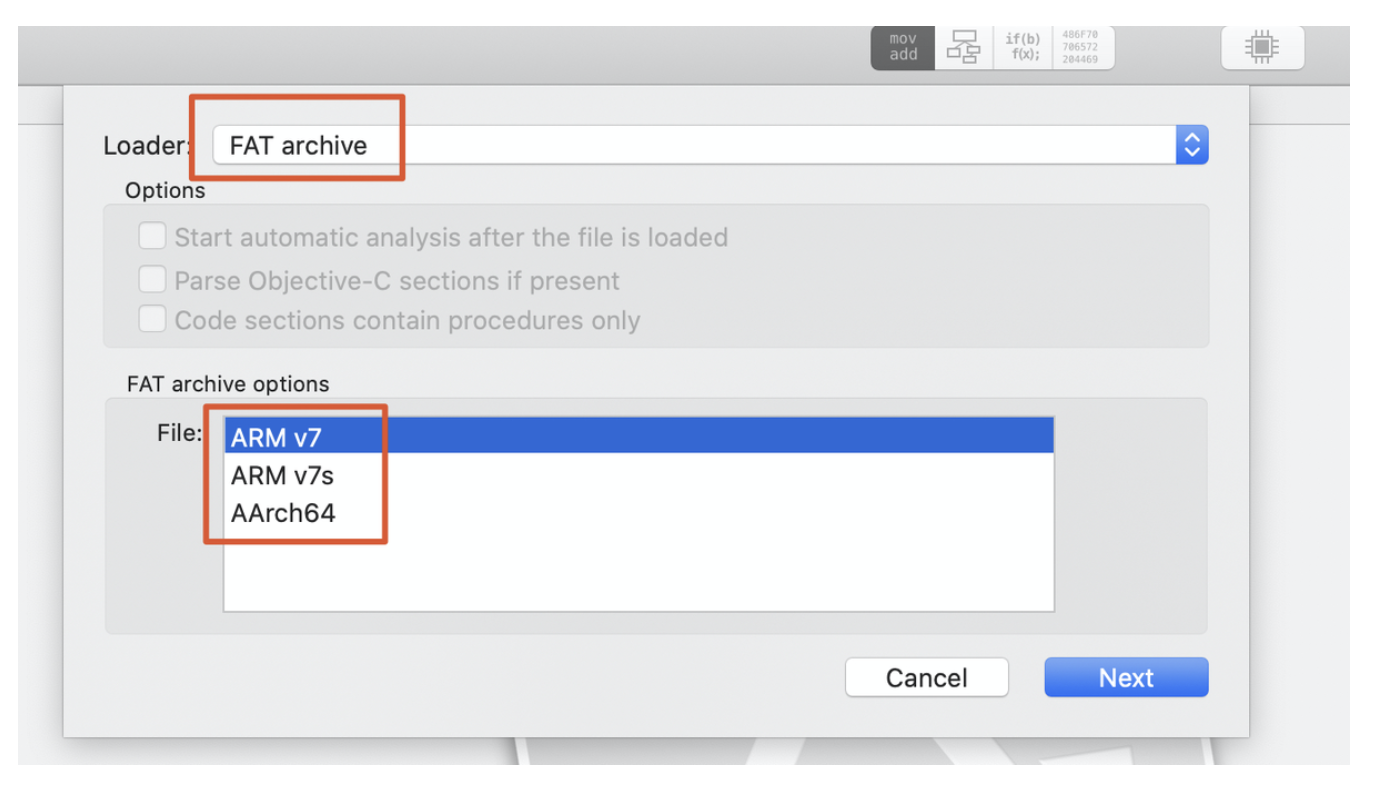
2.2lipo命令
lipo是管理Fat File的工具,可以查看cpu架构,,提取特定架构,整合和拆分库文件。
使用lipo -info 可以查看MachO文件包含的架构lipo -info MachO文件
lipo -info TestDsym
Architectures in the fat file: TestDsym are: armv7 armv7s arm64lifo –thin 拆分某种架构lipo MachO文件 –thin 架构 –output 输出文件路径lipo TestDsym -thin armv7 -output macho_armv7
lipo TestDsym -thin arm64 -output macho_arm64
file macho_armv7
macho_armv7: Mach-O executable arm_v7
file macho_arm64
macho_arm64: Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64lipo -create 合并多种架构lipo -create MachO1 MachO2 -output 输出文件路径lipo -create macho_armv7 macho_arm64 -output macho_v7_64
file macho_v7_64
macho_v7_64: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [arm_v7:Mach-O executable arm_v7] [arm64:Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64]
macho_v7_64 (for architecture armv7): Mach-O executable arm_v7
macho_v7_64 (for architecture arm64): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64三、MachO文件结构
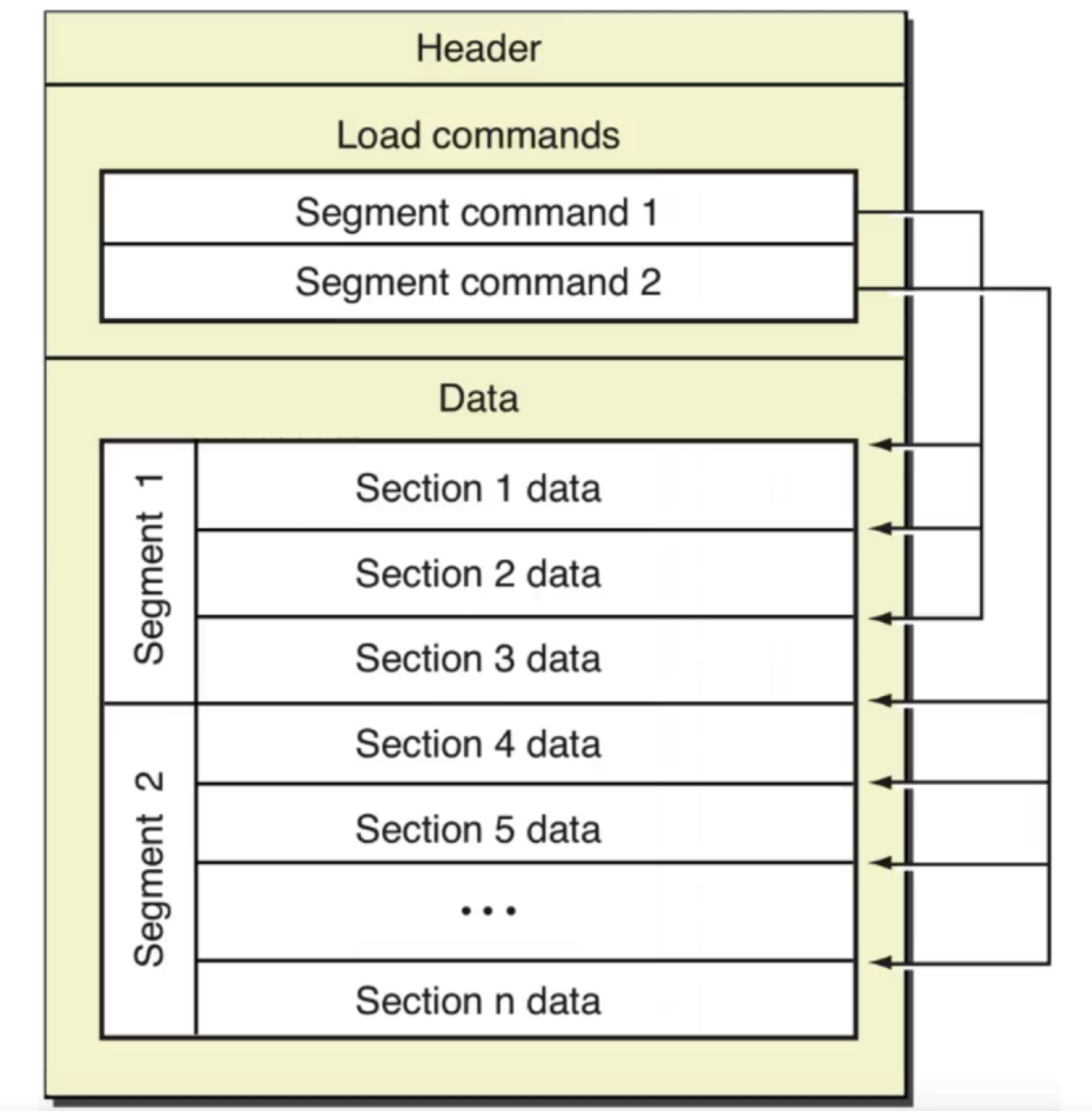
Mach-O 的组成结构如图所示:
Header:包含该二进制文件的一般信息。- 字节顺序、架构类型、加载指令的数量等。
- 快速确认一些信息,比如当前文件用于
32位还是64位,对应的处理器是什么、文件类型是什么。
Load Commands:一张包含很多内容的表。- 内容包括区域的位置、符号表、动态符号表等。
Data:通常是对象文件中最大的部分。- 包含
Segement的具体数据
- 包含
通用二进制文件就是包含多个这种结构。
otool -f MachO文件查看Header信息:
otool -f TestDsym
Fat headers
fat_magic 0xcafebabe
nfat_arch 3
architecture 0
cputype 12
cpusubtype 9
capabilities 0x0
offset 16384
size 79040
align 2^14 (16384)
architecture 1
cputype 12
cpusubtype 11
capabilities 0x0
offset 98304
size 79040
align 2^14 (16384)
architecture 2
cputype 16777228
cpusubtype 0
capabilities 0x0
offset 180224
size 79760
align 2^14 (16384)分析MachO最好的工具就是 MachOView了:
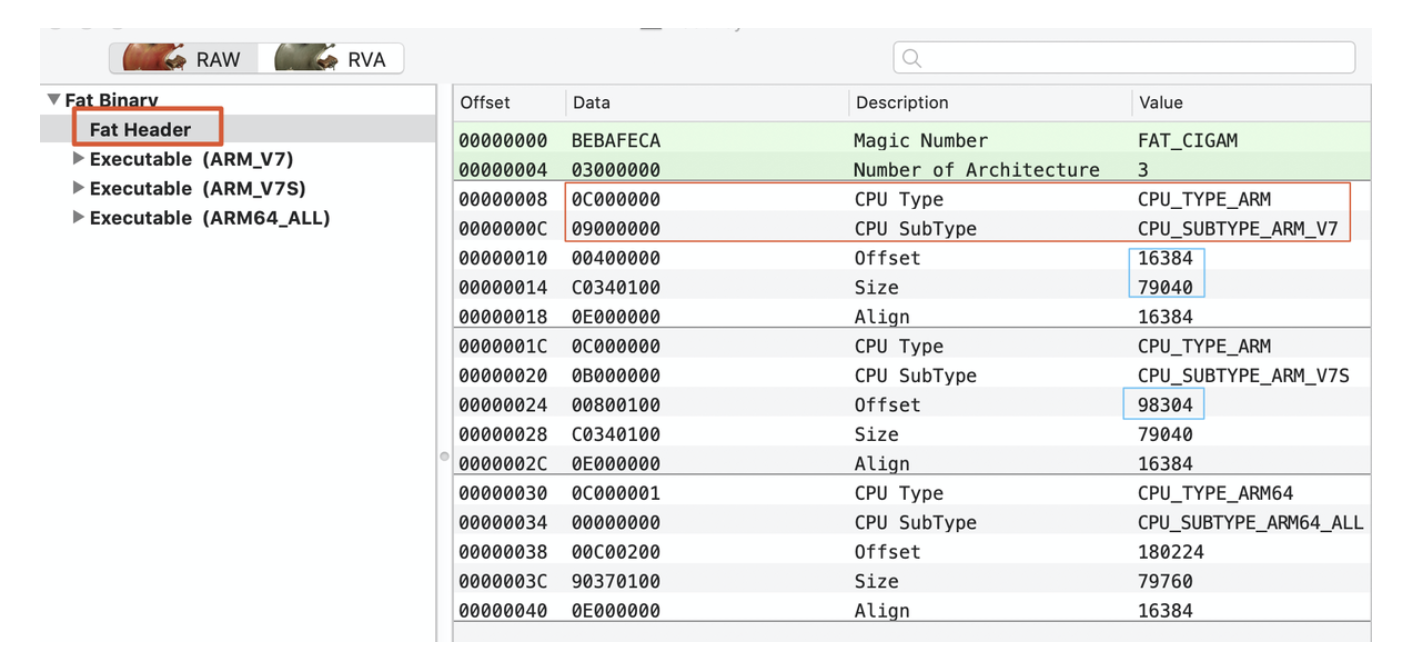
otool的内容相同,对于多架构MachO会有一个Fat Header其中包含了CPU类型和架构。Offset和Size代表了每一个每一个架构在二进制文件中的偏移和大小。这里有个问题是16384+79040 = 95424 < 98304,98304 - 16384 = 81920。81920 / 4096 / 4 = 5,可以验证这里是以页对齐的。(iOS中一页16K,MachO中都是以页为单位对齐的,这也就是为什么能在Load Commands中插入LC_LOAD_DYLIB的原因。)。
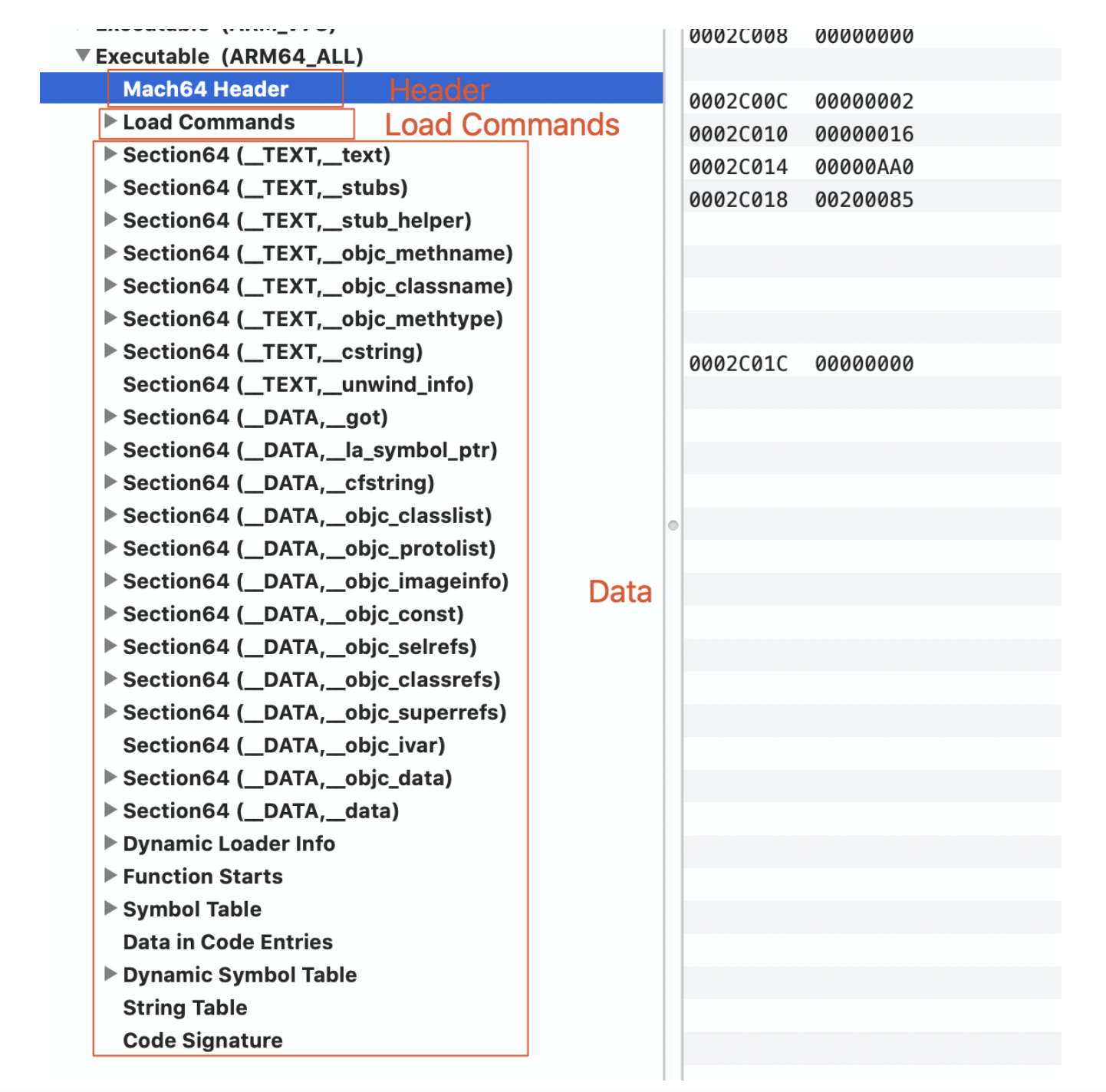
MachO对应结构如下:
3.1Header
Header数据结构:

对应dyld的定义如下(loader.h):
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};magic:魔数,快速定位属于64位还是32位。cputype:CPU类型,比如ARM。cpusubtype:CPU具体类型,arm64,armv7。filetype:文件类型,比如可执行文件,具体包含类型如下:#define MH_OBJECT 0x1 /* relocatable object file */
#define MH_EXECUTE 0x2 /* demand paged executable file */
#define MH_FVMLIB 0x3 /* fixed VM shared library file */
#define MH_CORE 0x4 /* core file */
#define MH_PRELOAD 0x5 /* preloaded executable file */
#define MH_DYLIB 0x6 /* dynamically bound shared library */
#define MH_DYLINKER 0x7 /* dynamic link editor */
#define MH_BUNDLE 0x8 /* dynamically bound bundle file */
#define MH_DYLIB_STUB 0x9 /* shared library stub for static
linking only, no section contents */
#define MH_DSYM 0xa /* companion file with only debug
sections */
#define MH_KEXT_BUNDLE 0xb /* x86_64 kexts */
#define MH_FILESET 0xc /* a file composed of other Mach-Os to
be run in the same userspace sharing
a single linkedit. */ncmds:Number of Load Commands,Load Commands条数。sizeofcmds:Size of Load Commands,Load Commands大小。flags:标识二进制文件支持的功能,主要是和系统加载、链接有关。reserved:arm64特有,保留字段。3.2 LoadCommands
Load Commands指示dyld如何加载二进制文件。一个基本的
Load Comands如下:
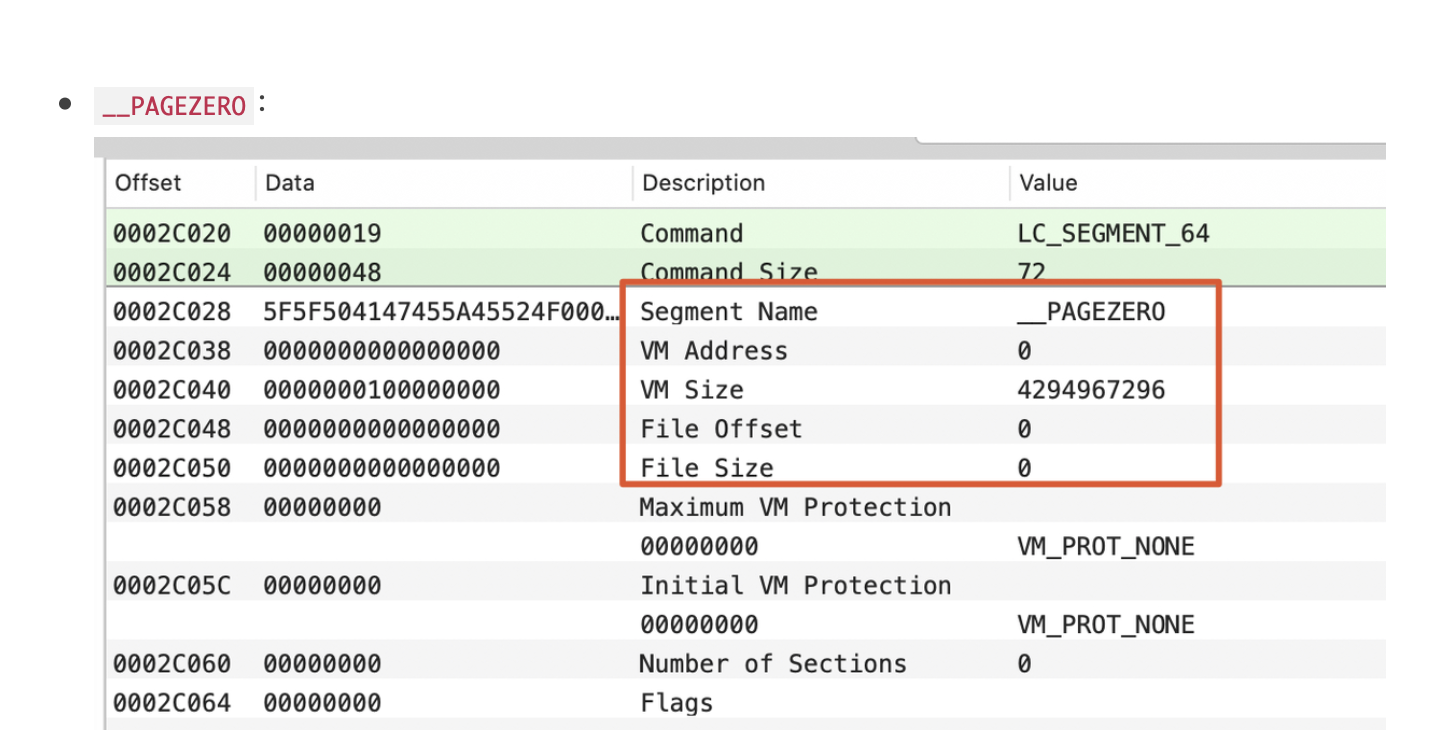
32位指令完全分开。(32位地址在4G以下,64位地址大于4G 0xffffffff = 4G)。__PAGEZERO不占用数据(file size为0),唯一有的是VM Size(arm64 4G,armv7比较小)。VM Addr : 虚拟内存地址VM Size: 虚拟内存大小。运行时刻在内存中的大小,一般情况下和File size相同,__PAGEZERO例外。File offset:数据在文件中偏移量。File size: 数据在文件中的大小。我们定位是看
VM Addr + ASLR。__TEXT、__DATA、__LINKEDIT:将文件中(32位/64位)的段映射到进程地址空间中。
分为三大块,分别对应DATA中的Section(__TEXT + __DATA)、__LINKEDIT。告诉dyld占用多大空间。
LC_DYLD_INFO_ONLY:动态链接相关信息。
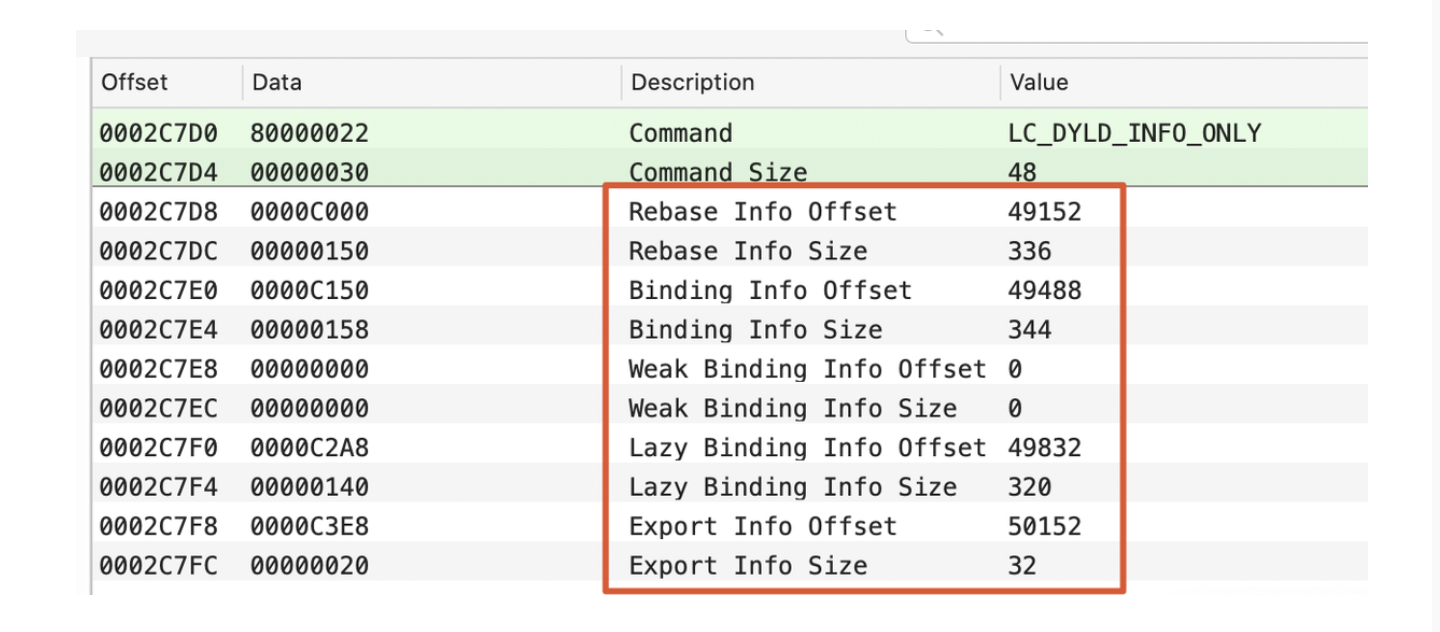
Rebase:重定向(ASLR)偏移地址和大小。从Rebase Info Offset + ASLR开始加载336个字节数据。Binding:绑定外部符号。Weak Binding:弱绑定。Lazy Binding:懒绑定,用到的时候再绑定。Export info:对外开放的函数。LC_SYMTAB:符号表地址。
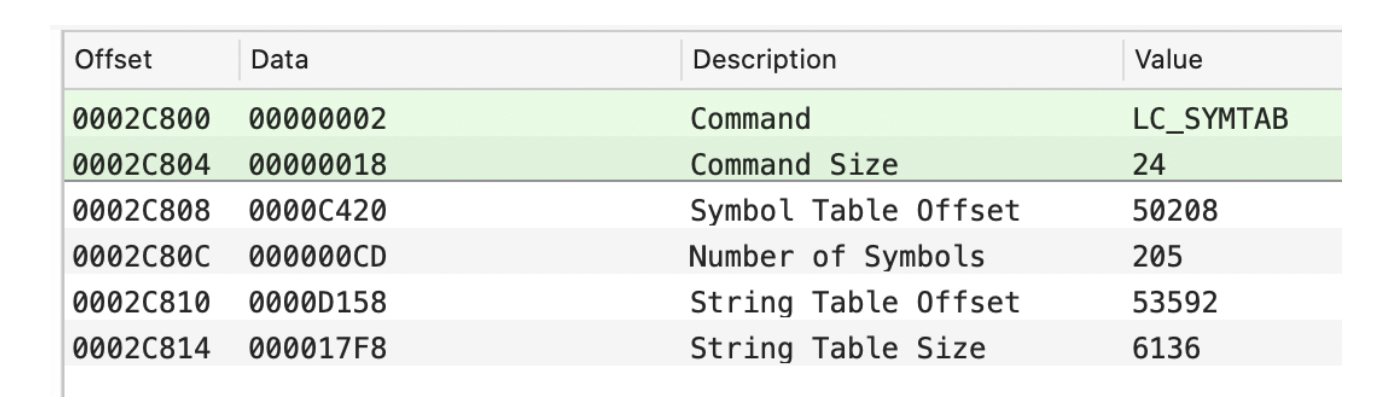
LC_DSYMTAB:动态符号表地址。
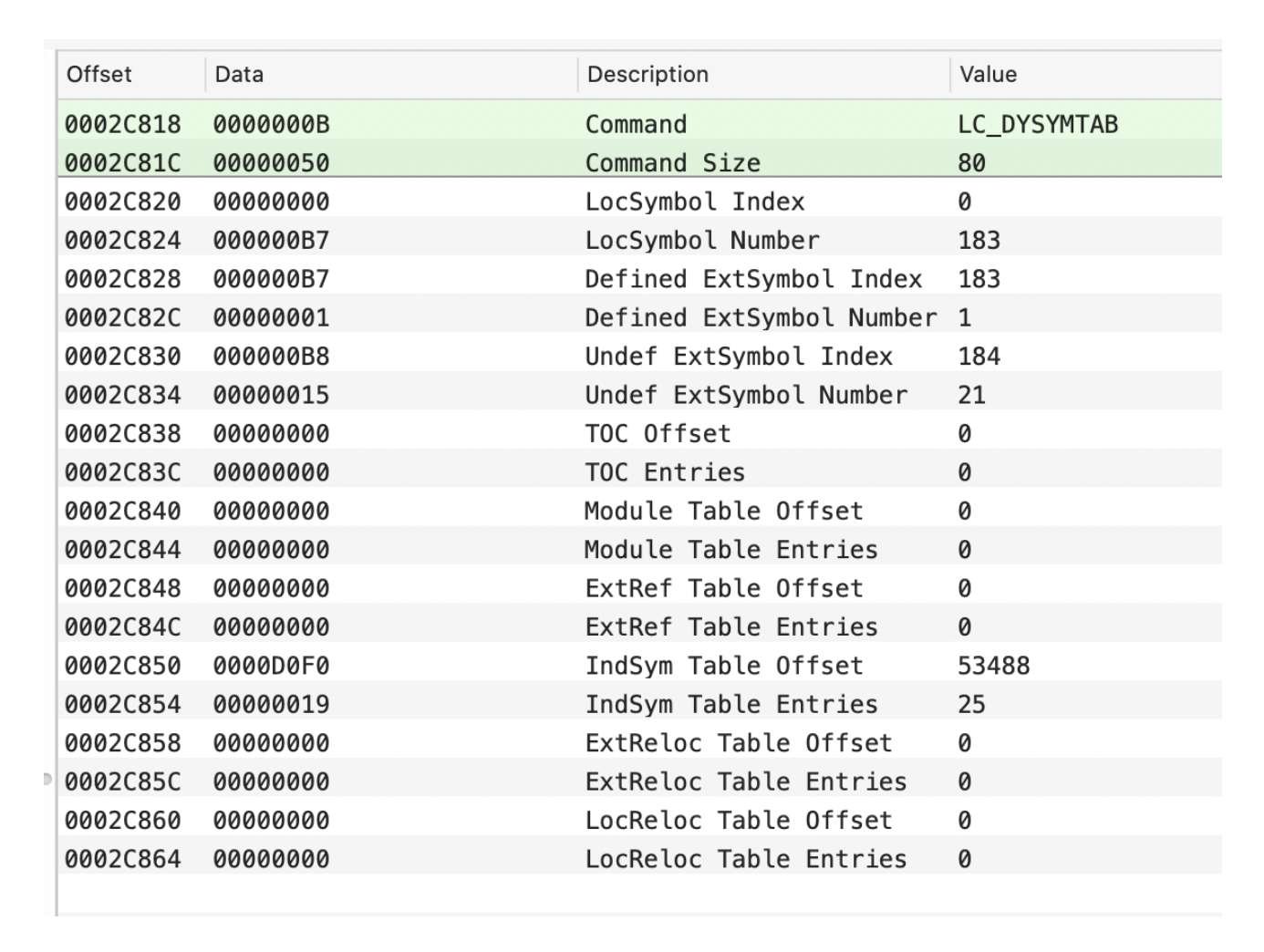
LC_LOAD_DYLINKER:使用何种动态加载器。iOS使用的是dyld。
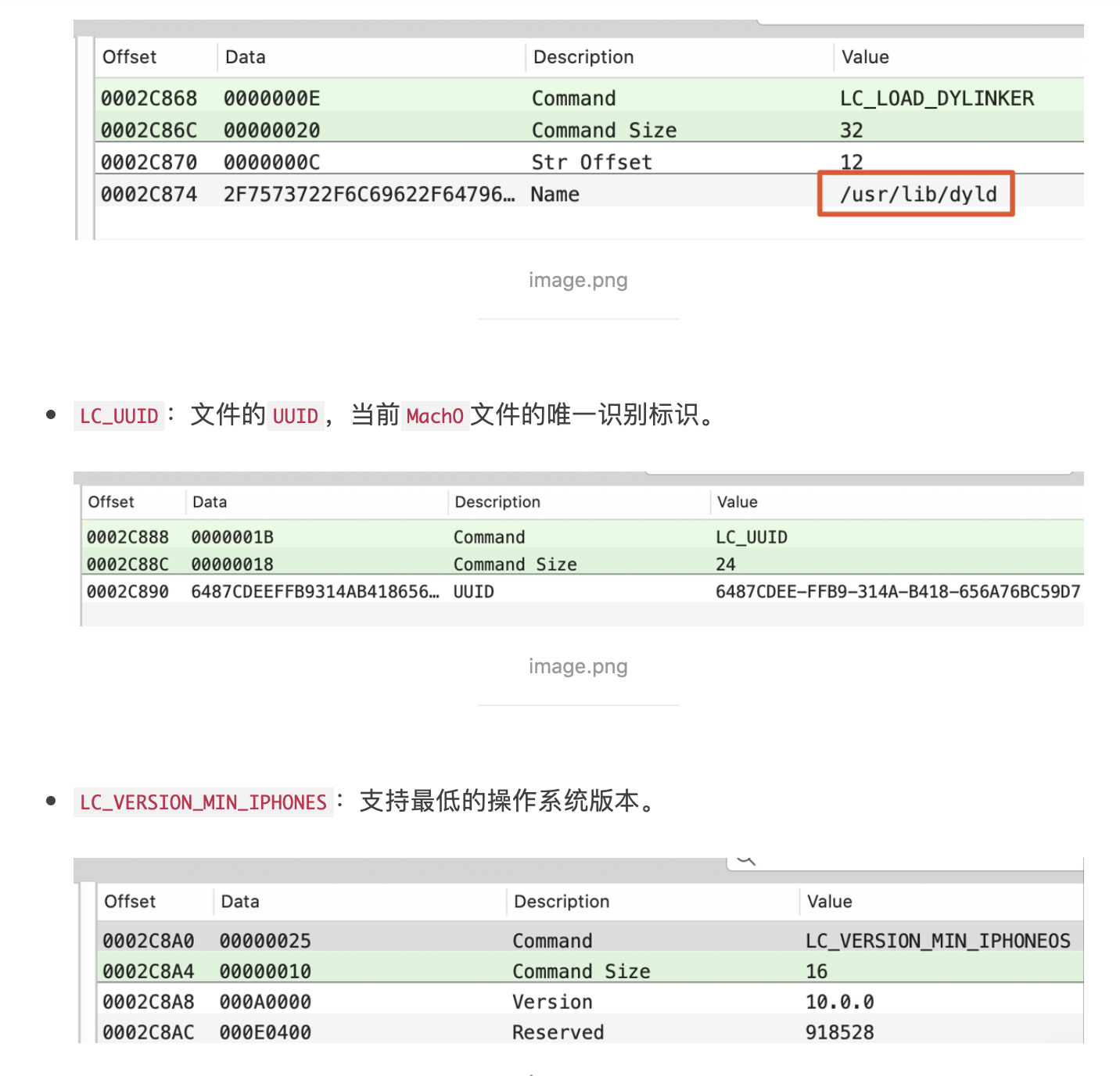
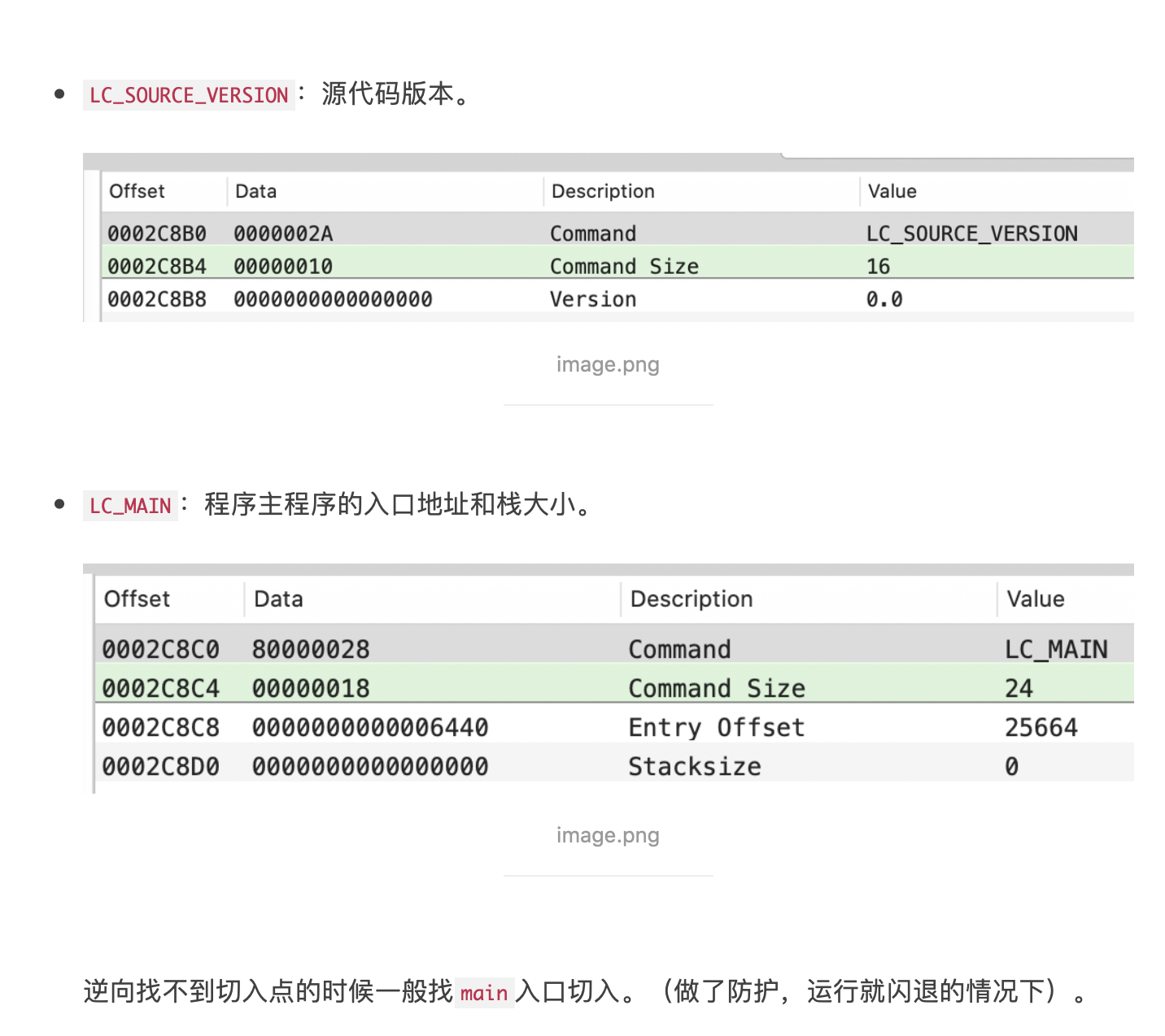
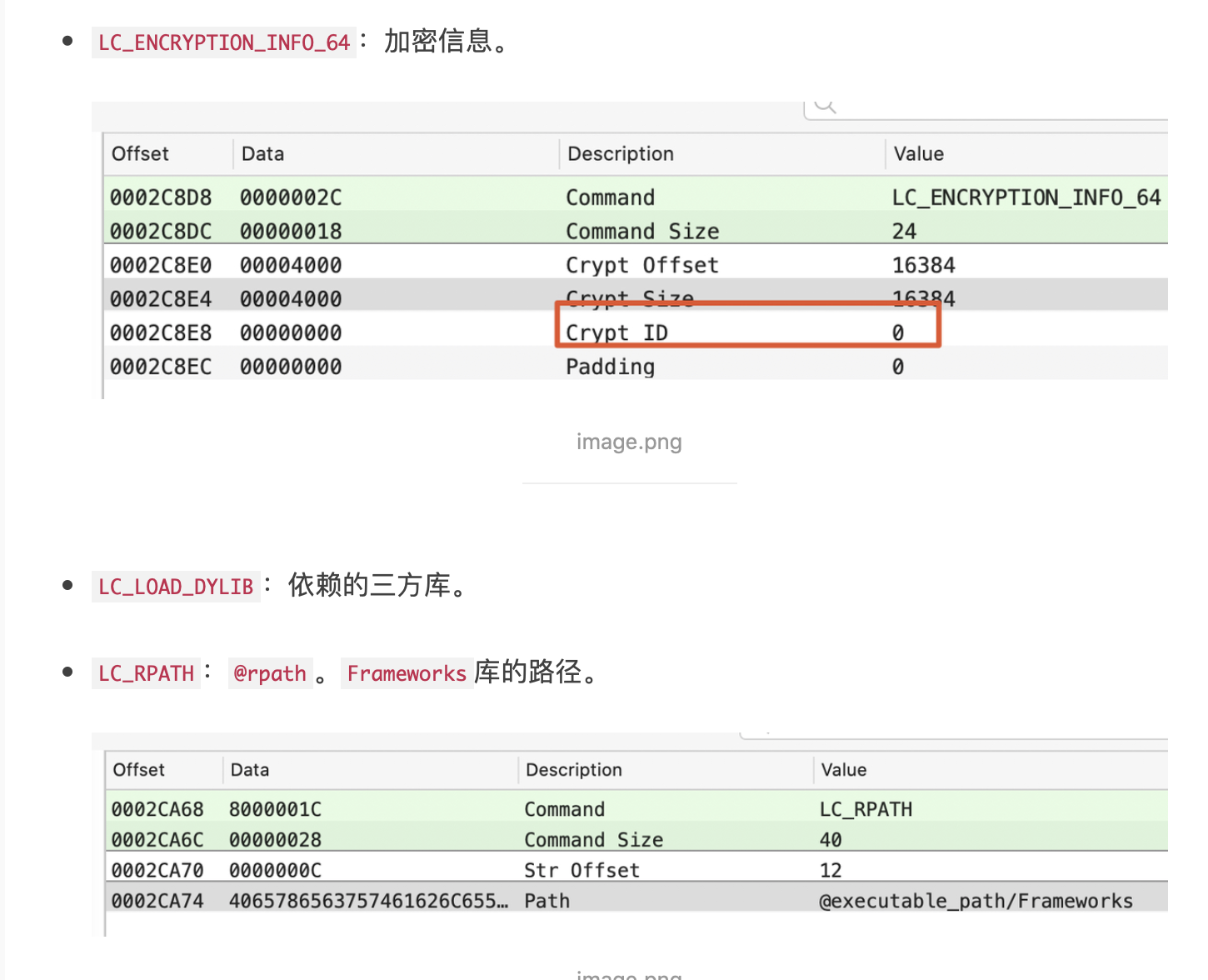
LC_FUNCTION_DYLIB:函数起始地址表。LC_DATA_IN_CODE:定义在代码段内的非指令的表。LC_DATA_SIGNATURE:代码签名。
3.3Data
Data包含Section(__TEXT + __DATA)、__LINKEDIT。
3.3.1__TEXT
__TEXT代码段,就是我们的代码。
__text:主程序代码。开始是代码起始位置,和Compile Sources中文件顺序有关。
__stubs & __stub_helper:用于符号绑定。

65a0就是325a0,这里是循环做符号绑定。__objc_methname:方法名称__objc_classname:类名称__objc_methtype:方法类型__cstring:字符串常量
3.3.2__DATA
__DATA数据段。
__got&__la_symbol_ptr:外部符号有两张表Non-Lazy和Lazy。
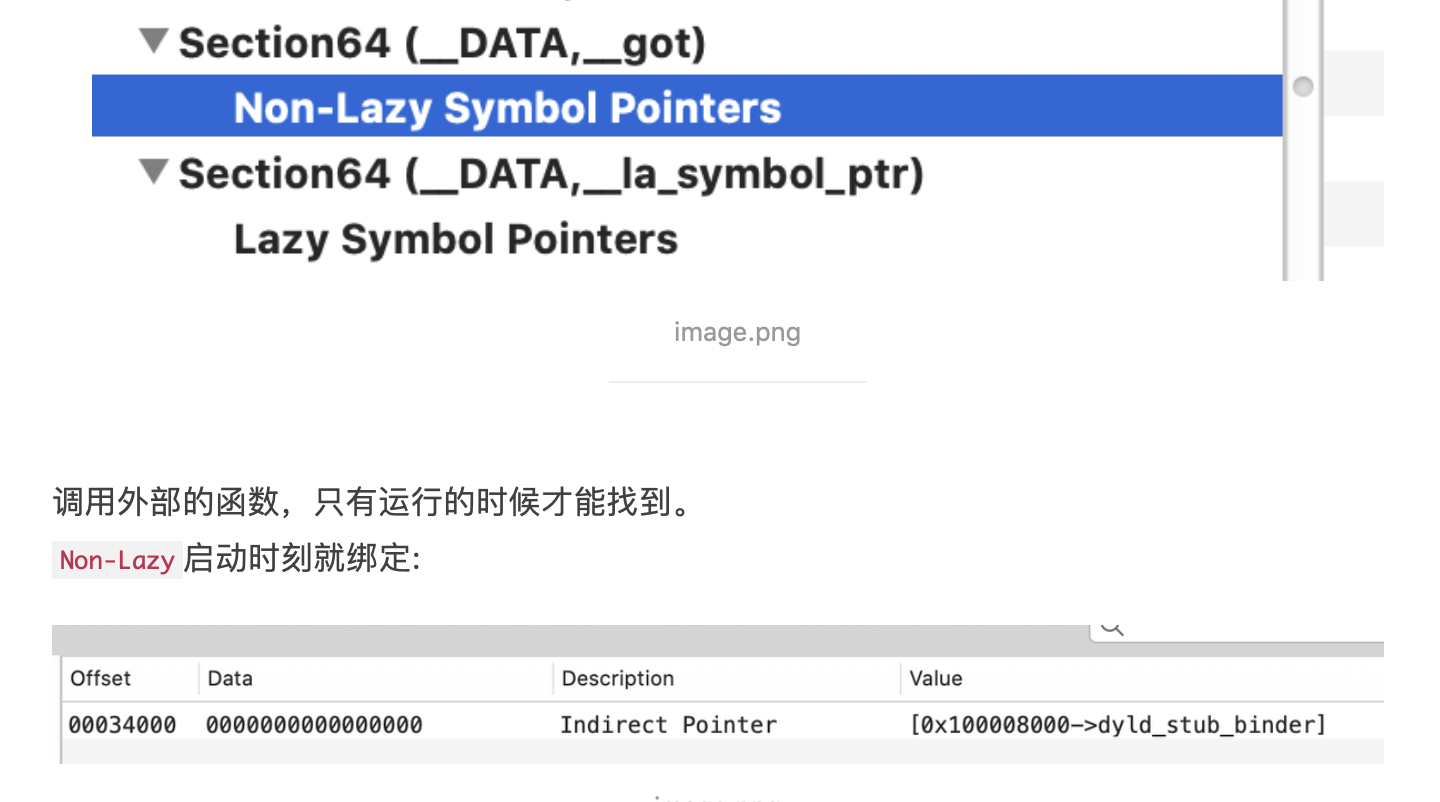
Lazy懒加载表,表中的指针一开始都指向 __stub_helper:
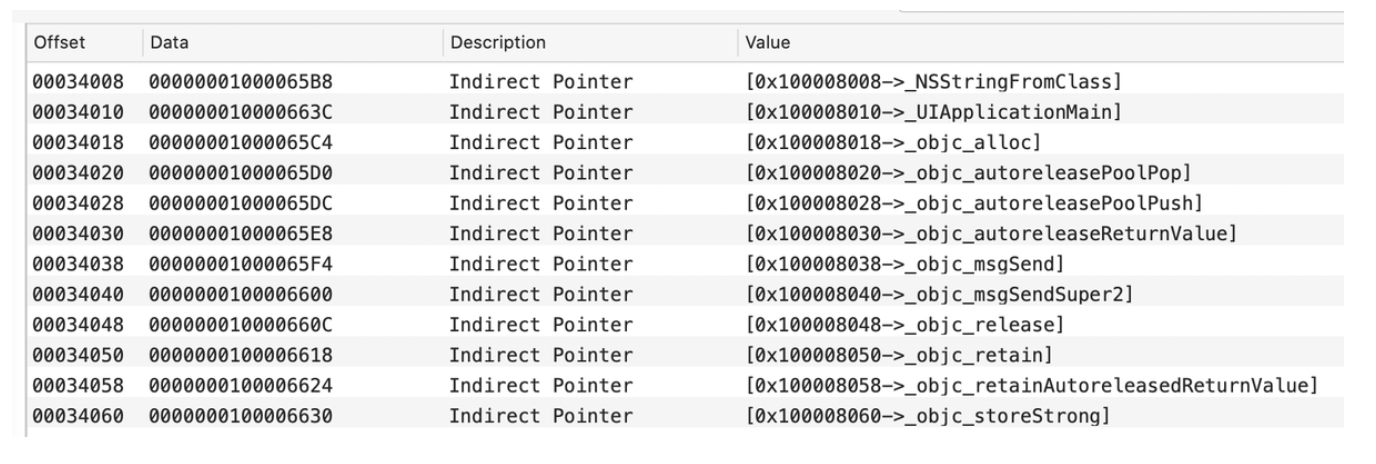
__cfstring:程序中使用的Core Foundation字符串(CFStringRefs)。__objc_classlist:类列表。__objc_protolist: 原型。__objc_imageinfo:镜像信息
__objc_selrefs:self引用__objc_classrefs:类引用__objc_superrefs:超类引用__data:初始化过的可变数据。
3.3.3 __LINKEDIT
Dynamic Loader Info:动态加载信息
Function Starts:入口函数
Symbol Table:符号表
Dynamic Symbol Table:动态库符号表
String Table:字符串表
Code Signature:代码签名
总结
MachO属于一种文件格式。- 包含:可执行文件、静态库、动态库、dyld等。
- 可执行文件:
- 通用二进制文件(Fat):集成了多种架构。
lipo命令:-thin拆分架构,-creat合并架构。
MachO结构:Header:快速确定该文件的CPU类型,文件类型等。Load Commands:知识加载器(dyld)如何设置并加载二进制数据。Data:存放数据,代码、数据、字符串常量、类、方法等。
作者:HotPotCat
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9f6955575213
